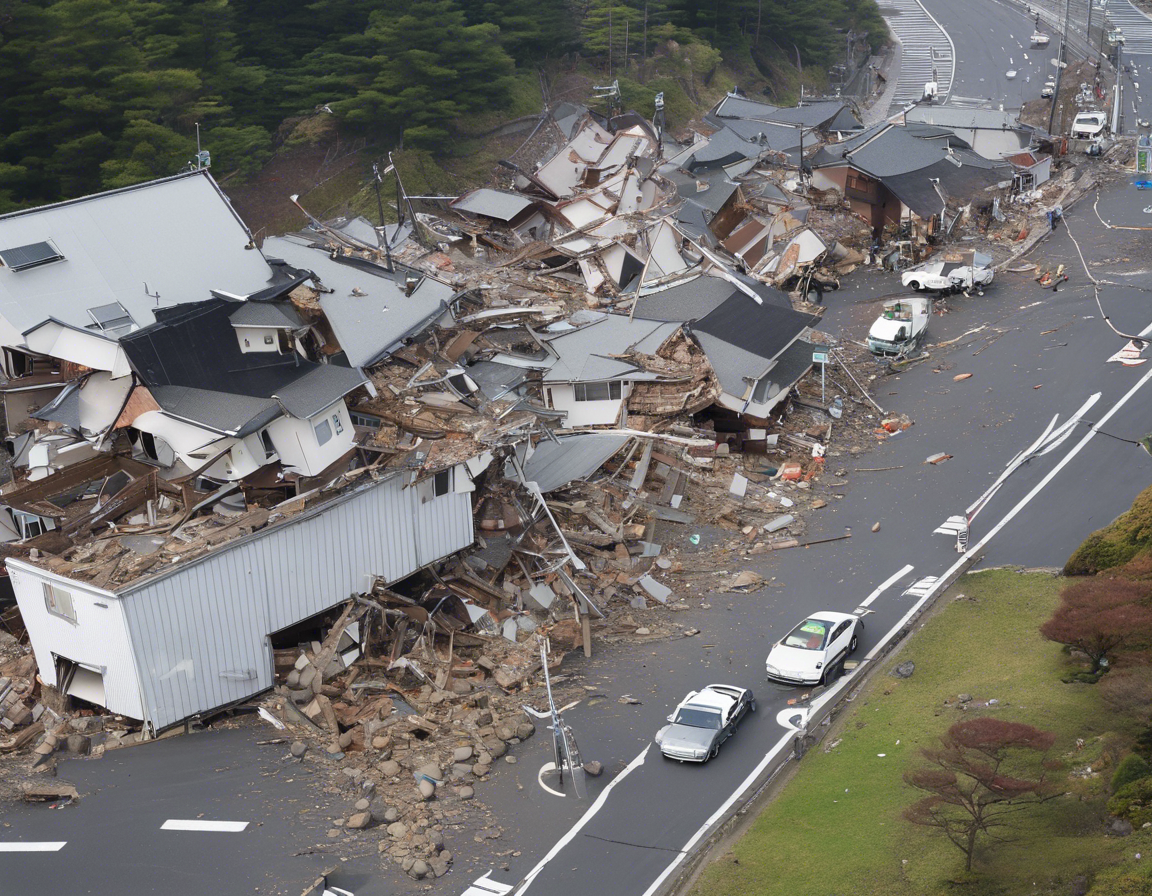
Amidst the natural calamities that frequently occur around the world, Japan recently experienced a significant seismic event, with a 6.0-magnitude earthquake striking the region. The tremors were felt across the affected areas, causing disruptions and reminding everyone of the ever-present threat of geological hazards. In this blog post, we will explore the implications of this earthquake, its impact on Japan, and the broader context of seismic activity in the region.
Understanding Earthquakes in Japan
Japan is situated along the Pacific Ring of Fire, making it highly prone to earthquakes due to the tectonic plates beneath the Earth’s surface. The subduction zone where the Pacific Plate dives beneath the Eurasian Plate has led to the formation of the Japanese archipelago and a complex network of fault lines. These geological dynamics mean that earthquakes are not uncommon in Japan, and the country has implemented robust infrastructure and preparedness measures to mitigate the potential damages caused by such seismic events.
The Recent 6.0 Earthquake
The 6.0-magnitude earthquake that struck Japan recently had its epicenter located in a seismically active zone, which amplified its effects. The tremors were felt across densely populated areas, including major cities and towns, leading to concerns about potential structural damage and casualties. The Japanese Meteorological Agency issued alerts and advisories to inform the public and authorities about the earthquake and its aftershocks.
Impact on Infrastructure
The intensity of a 6.0-magnitude earthquake can cause varying levels of damage to infrastructure, depending on factors like building design, soil type, and proximity to the epicenter. In Japan, where stringent building codes are enforced to withstand seismic activities, damage to infrastructure was relatively limited. However, older buildings and structures may have experienced cracks or structural weaknesses, necessitating thorough inspections and potential renovations.
Response and Rescue Operations
Following the earthquake, emergency response teams and local authorities swiftly mobilized to assess the situation, provide assistance to those in need, and ensure public safety. Search and rescue operations were conducted in affected areas to locate any individuals trapped under debris and to address any immediate medical concerns. The collaborative efforts of emergency responders, community volunteers, and government agencies were crucial in managing the aftermath of the earthquake.
Preparedness and Resilience
Japan’s proactive approach to disaster preparedness and resilience has been instrumental in mitigating the impacts of earthquakes and other natural disasters. The nation has invested heavily in early warning systems, public education campaigns, and seismic retrofitting of buildings to enhance their ability to withstand earthquakes. As a result, Japan has been able to limit the loss of life and property damage in the face of frequent seismic activities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Earthquakes in Japan
1. How common are earthquakes in Japan?
Earthquakes are relatively common in Japan due to its location along the Pacific Ring of Fire. The country experiences thousands of seismic events each year, ranging from minor tremors to major earthquakes.
2. What is the role of the Japanese Meteorological Agency in earthquake monitoring?
The Japanese Meteorological Agency plays a crucial role in monitoring seismic activities, issuing alerts and warnings, and providing real-time information to the public and relevant authorities to ensure preparedness and safety.
3. How do buildings in Japan withstand earthquakes?
Japanese buildings are constructed using advanced engineering techniques and technologies that enhance their resilience to seismic activities. Features such as base isolation systems, damping devices, and flexible building designs help structures withstand tremors and minimize damage.
4. What should residents do during an earthquake in Japan?
During an earthquake, residents in Japan are advised to follow safety protocols, such as taking cover under sturdy furniture, staying away from windows, and evacuating buildings if necessary. Being prepared with emergency kits and having a family emergency plan in place are also crucial.
5. How does Japan prepare for tsunamis that may follow earthquakes?
In addition to earthquake preparedness, Japan has implemented robust tsunami warning systems, coastal barriers, and evacuation plans to mitigate the impact of tsunamis triggered by seismic events. Regular drills and public awareness campaigns help ensure readiness in coastal communities.
6. What lessons can other countries learn from Japan’s approach to earthquake preparedness?
Other countries can learn valuable lessons from Japan’s comprehensive approach to earthquake preparedness, including investing in early warning systems, enforcing strict building codes, conducting regular drills, and fostering a culture of resilience among the population.
7. Are there ongoing research and innovations in earthquake preparedness in Japan?
Japan continues to invest in research and innovations related to earthquake preparedness, including developing advanced seismic monitoring technologies, enhancing building retrofitting techniques, and exploring new ways to increase community resilience in the face of natural disasters.
8. How does Japan coordinate international collaboration for disaster response in the aftermath of earthquakes?
Japan actively participates in international collaborations and agreements for disaster response and humanitarian assistance. Through platforms like the United Nations Disaster Assessment and Coordination, Japan coordinates with global partners to provide support and resources during times of crisis.
9. What are the long-term implications of frequent earthquakes on Japan’s infrastructure and economy?
The cumulative impact of frequent earthquakes on Japan’s infrastructure and economy includes the costs of rebuilding and retrofitting structures, disruptions to transportation and utilities, and implications for insurance and financial markets. Developing sustainable solutions and resilient infrastructure is essential for mitigating these long-term effects.
10. How can individuals contribute to earthquake preparedness in Japan and globally?
Individuals can contribute to earthquake preparedness by staying informed about potential risks, creating personal emergency kits, participating in community drills, supporting local disaster response organizations, and advocating for policies that promote resilience and sustainability in their communities.
In conclusion, the recent 6.0-magnitude earthquake in Japan serves as a reminder of the constant threat posed by seismic activities. By prioritizing disaster preparedness, investing in resilient infrastructure, and fostering a culture of safety and collaboration, Japan continues to set an example for effective earthquake mitigation strategies. As we navigate the uncertainties of the natural world, learning from experiences such as this earthquake can help us better protect our communities and build a more resilient future.